The Role of Trade in Services in Economic Development.
Trade in services has increased in importance over the last two decades with the advent of globalization. Today, more than 60% of the most of the Western economies are irk service sector.
Trade in services has been playing an important role in economic development. Following points explain the role of trade in.services:
Employment:
Services sector provides jobs to millions of people. Services sector is relatively more labor-intensive and, therefore, larger service exports mean greater employment opportunities for the work force. Following table offers an international comparison of employment:
Also Read | What is SIP – Systematic Investment Plan?
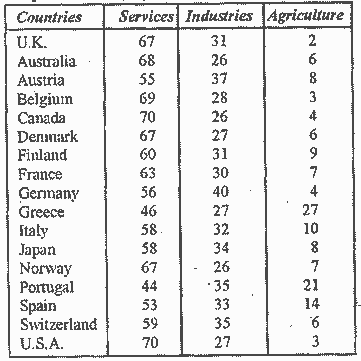
From the above table we find that with the exception of Greece and Portugal, all the countries have more than 50% employment in services sector.
Services account for about 30% and 30% to 50% in case of low income and middle income developing countries respectively.
Also Read | Best water bottle of the year
Tourism, hoteling, manpower, software and turnkey project exports and consultancy assignments are highly labor-intensive and meet the requirements of developing countries by helping them in solving their unemployment problems.
Share in GDP:
Services sector has been a major contributor to GDP of many countries. The services sector accounts for more than 70% of GDP in many countries, Presently, India’s service sector constitute over 42% of GDP though per capita income in just above $ 350 per annum.
While the share of value added by services in GDP increased from 38 per cent in 1980 to 42 per cent in 1997 for the low-income economies, the corresponding figure were 40 and 50% for the middle-income economies and above 60% for the high-income economies.
Also Read | The Ways to Show Intelligence of Intelligent People Without Saying Anything.
The services sector has been growing at a rate faster than that of GDP for the low and middle-income economies, but not for high-income economies.
In case of India, the share of value-added by services in GDP Increased from 36% 1980 to 43% in 1997. While GDP grew at an average annual rate of 5.8% during the period 1980-90 and by 5.9% during 1990-97, the corresponding growth rates for the value-added by services were 6.7 and 7.5% respectively.
Source of Foreign Exchanges:
Services have emerged as an important source of foreign exchange earnings for both the developed and developing countries.
Also read | The Rights of an Unpaid Seller.
Today cross border transactions in services alone exceed 1 trillion US dollars per annum and these account for about 20% of the total world trade.
World exports of goods and commercial services averaged 6.6 trillion dollars annually during the triennium ending 1997, including 1.3 trillion dollars worth of exports, of services accounting for 20% of total world exports (IMP, 1998).
While the export of services accounts for 17% of developing country exports, the corresponding share is higher at 21% for industrial countries.
The share of developing countries in the world export of services increased from 22.3% in 1991 to 29.3% in 1997. The share of Asian developing countries in total world exports increased from 9.9% to 15.2% during this period.
Also read | The rules relating to delivery of goods under the Sale of Goods Act.
Exports of services such as tourism, shipping, telecommunication, insurance, banking, software and project exports including technical consultancy and legal management have come to occupy a strategic position in the world markets.
Especially in the case of many developing countries, surplus in the invisible account have greatly helped them in mitigating deficit problems in their balance of payments account.
Economic Growth:
Services constitute infrastructure of an economy. Services accelerate the process of economic growth. Economic infrastructure offers services which are essential for the growth of agriculture and industries.
Also read | The doctrine of Caveat Emptor.
For example, growth of agriculture and industrial production is not possible without transport and communication. Financial services promote inducement to invest.
For example, when funds are easily available through banks and other financial institutions entrepreneurs are induced to make investment. By offering infrastructural services in the backward regions, we can speed up the process of economic growth in these areas.
Also Read | Common Habits of Deeply Angry People
Economic infrastructure proves helpful in the globalization of the economy. It is largely because of these services in an efficient and adequate manner that the developed countries have been able to attain higher levels of economic development.


