What is different between Star Topology and Bus Topology?
Star Topology.
It is one of the most common network setups where each of the devices and computers on a network connect to a central hub. The hub is connected to all the nodes directly. Each computer is interconnected indirectly to each other. A hub is used to expand one network connection into many. In small networks we use single hub and in larger we use many.
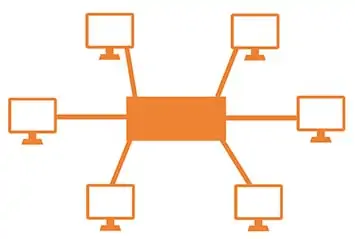
Advantages of Star Topology
- It is more reliable.
- Failing of one connection does not disturb the network, it can be isolated by hub.
- It is easy to replace, install or remove hosts or other devices.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
- Performance is fast.
Limitations of Star Topology
- Costly network topology.
- The network will not work if the hub is not functioning.
- Usually, a device is needed to switch the network traffic.
Bus topology is a network setup where each of the computers and network devices are connected to a single cable or backbone.
The computers are connected with single communication cable. It allows only one computer to send a message at a time. The more the number of computers attached to it, lesser will be the speed. A node can transmit the data when it finds the bus free, means when the bus is busy it has to wait. Each node connected to the network has a unique address, which is used by the operating system to keep track of data transmission.
It is the most common and simple topology used in networking. The nodes are connected a single wire called backbone. The nodes wait for their turn and then send or receive data or messages. For this, the unique addresses assigned play a help.
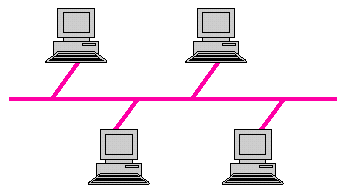
Advantages of Bus Topology
- It is simple to use.
- It is reliable.
- Cost effective.
- Scope of extension is there, and it is easy to implement.
- Failure of one node will not disturb others.
Limitations of Bus Topology
- A computer has to wait for its turn to come.
- Number of computers can affect speed of LAN.
- If extended, the speed will get affected.
- Nodes are connected using terminators at both the ends of the cable.